Science
THE SCIENCE BEHIND TCP-25
TCP-25 originates from groundbreaking research at Lund University, where Professor Arthur Schmidtchen and team identified a class of thrombin-derived peptides with potent anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. These peptides are part of the innate immune system, the body’s immediate response to injury. By replicating this natural defense mechanism in a controlled, therapeutic form, TCP-25 addresses key drivers of dysfunctional healing at the molecular level.
TCP refers to thrombin-derived C-terminal peptides, short amino acid sequences that occur naturally in wounds and play an active role in the healing process. Xinnate’s lead candidate drug, TCP-25 Gel, is based on one of these multifunctional peptides, known as TCP-25. Its mode of action is well studied and understood, and TCP-25 Gel has demonstrated proven therapeutic effects on infection, inflammation, and healing.

Professor Artur Schmidtchen
Modes of action
Dampening the immune response
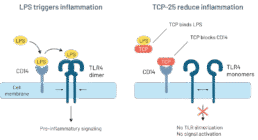
Binds to PAMPs
TCP-25 binds specifically to and neutralizes immune stimulating products released from microorganisms (i.e. PAMPs), such as LPS, LTA, peptidoglycan, lipid A, resulting in a reduction of the strong inflammatory response caused by these molecules.
Blocks CD14
TCP-25 also binds to CD14, a receptor for PAMPs expressed on innate immune cells (e.g. macrophages), and blocks the PAMP-binding site of CD14, preventing dimerization of toll-like receptors (TLR) and inflammatory signaling. This leads to down-regulation of excessive levels of cytokines and chemokines (e.g. TNF-ɑ, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1 and IL-1ß) in wounds, thus promoting normal healing. It also leads to reduction of Heparin Binding Protein (HBP) and the reduction of wound exudation.
Neutralizing microorganisms
Kills bacteria
TCP-25 also has a direct antimicrobial effect by interacting with bacterial and fungal membranes, leading to membrane disintegration, permeabilization and microbial killing. TCP-25 addresses both gram positive and negative bacteria and is also effective on antimicrobial resistant bacteria (AMR).
Preserves immune clearance
Furthermore, TCP-25 does not interfere with bacterial phagocytosis by the immune system, allowing retained phagocytic clearance and reduced bacteria-induced inflammation.
The proprietary gel formulation developed for TCP-25 Gel preserves the multimodal action of TCP-25.
Results
An extensive preclinical development package has been finalized with reassuring results supporting clinical development of TCP-25 Gel. Based on this, TCP-25 Gel entered clinical development with a completed phase 1 study demonstrating its safety and preliminary efficacy in healthy volunteers with induced wounds, patients with large complex wounds (VLU) and patients with Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) wounds.
The efficacy of TCP-25 Gel has been demonstrated in relevant animal wound models of bacterial infection and inflammation and proven to be superior to widely used benchmarks containing PHMB or silver.
Effects of TCP-25 Gel in a wound model
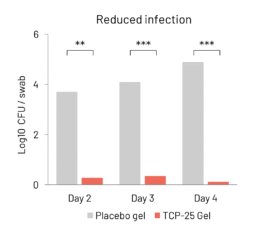
TCP-25 Gel reduces infection
Microbiological analysis of wounds from days 2, 3, and 4 of topical application of TCP-25 Gel in model of induced wounds
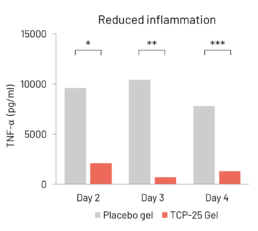
TCP-25 Gel reduces inflammation
Analysis of wound fluid cytokines collected on days 2, 3, and 4 of topical application of TCP-25 Gel in model of induced wounds
TCP-25 Gel improves wound healing
Clinical scoring of wounds after 3 days of topical application of TCP-25 Gel in model of induced wounds
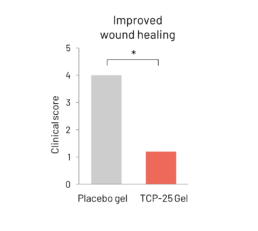
Reference: Puthia et al., Sci Transl Med. 2020 Jan 1;12(524)
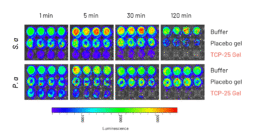
Direct effects of TCP-25 Gel on bacteria
In vitro antibacterial effects of TCP-25 gel
Bioluminescent S. aureus or P. aeruginosa bacteria were incubated with TCP-25 Gel and the bioluminescent signal was analyzed using bioimaging (IVIS Spectrum).
Publications
TCP-25 Gel is built on decades of research and the results have been published in leading scientific journals. See our publications here:
